DB FPX 8405 Assessment 5 Final Report
Student Name
Capella University
DB-FPX 8405 Effective Organizational Leadership
Prof. Name:
Date
Executive Summary
CapraTek aims to excel by defining and delivering technology solutions for future challenges. As a leading designer and manufacturer of computer server components, CapraTek continually provides innovative solutions to its customers. The company’s priority is digital innovation, especially as it plans to expand into emerging wireless technologies.
A business problem refers to a current or anticipated challenge a company may face. This report will examine three potential business problems for CapraTek in the areas of leadership, information technology systems, and marketing management. Each area will identify a specific issue that warrants a business project to address it. The report will also provide an overview of how these business problems relate to broader concerns faced by CapraTek and similar companies. Problem statements for leadership, information technology systems, and marketing management will be supported by scholarly evidence.
Each of the three areas will be illustrated with a fishbone diagram, a visualization tool for categorizing potential causes of identified problems. These diagrams will help CapraTek leadership narrow down the problems. A proposed Riipen project will be included for comparison and consideration of the leadership business problem. Riipen is an experiential learning platform that helps businesses find solutions for future challenges. The report will conclude with a summary of the main points of the proposed project, supported by Mind Map illustrations for each area.
DB FPX 8405 Assessment 5 Final Report
CapraTek’s vision is to excel in defining and delivering technology solutions for future challenges. As a leader in designing and manufacturing computer server components, CapraTek consistently provides innovative solutions to its customers. Digital innovation is a priority as the company expands into emerging wireless technologies. This report assesses CapraTek’s needs, providing information and resources to improve operational effectiveness. It identifies potential business problems in leadership, information systems, and marketing, supported by scholarly resources and proposed frameworks and theories. Each area is illustrated with a mind map to further support the suggestions.
Ryba (2021) highlights that aligning organizational goals with business plans differentiates high-performing companies from low-performing ones. Best practices involve clear organizational goals that support the mission, vision, and strategy, with significant support from leadership and communication at every level. The business-to-consumer (B2C) model, where products are sold directly from the business to consumers, is illustrated. The report includes best practices for creating a business plan aligned with organizational goals, along with a model and illustration.
Business to Consumer (B2C) Model
Leadership
The potential leadership business problem is insufficient training in resistance to change. This issue is relevant globally, as research by Beer et al. (2016) shows businesses spend significant amounts on training without a good return on investment. To assess and understand this problem at CapraTek, Yukl (2011) discusses the Leadership Contingency Theory, which explains how leadership situations alter a leader’s influence. This conceptual framework could be applied to CapraTek’s leadership problem to solve new and emerging practical issues.

Information Systems
The potential information systems problem is the lack of a current digital innovation strategy. This affects organizations across various platforms. Morgan (2019) notes that 70% of digital innovations fail, resulting in lost money, resources, time, and credibility. To understand this problem at CapraTek, Li and Chan (2019) discuss the dynamic capabilities framework, addressing IT capability, dynamic digital capability, dynamic IT management, and IT knowledge management capability. The task technology fit theory, defined by Goodhue and Thompson (1995) as the link between IT and individual performance, is suggested for further assessment. The dynamic capabilities framework can help CapraTek evolve its information systems capabilities.

Marketing
CapraTek is experiencing a loss in product sales, a significant issue for small businesses (Kokemuller, 2016). To understand this problem, Kotler et al. (1999) suggest a marketing theory with three levels: core, actual, and augmented. The conceptual framework, comprising the thought of the potential marketing problem, can be used to address new and emerging practical issues at CapraTek.

Potential Riipen Project
The proposed Riipen project is “Level-Up: Making Sense of Organizational Change.”
Project Scope: This research project allows students to explore organizational change and transformation processes, focusing on effective change. Activities include analyzing factors influencing change and the implications on stakeholders. Findings will inform organizational change management theory and practice (Riipen, n.d.).
Mind Leadership Mind Map
The leadership mind map includes framework, concept, and theory keywords on the right side, with keywords from the leadership fishbone diagram on the left side. It illustrates logical relationships among frameworks for leadership, marketing management, and information systems, providing a detailed explanation.

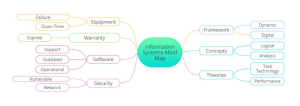
Information Systems Mind Map
Similarly, the information systems mind map includes relevant framework, concept, and theory keywords on the right side and keywords from the information systems fishbone diagram on the left. It illustrates logical relationships among frameworks for leadership, marketing management, and information systems, providing a detailed explanation.
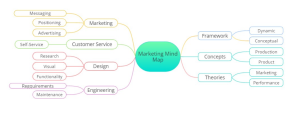
Marketing Mind Map
The marketing mind map includes relevant framework, concept, and theory keywords on the right side and keywords from the marketing fishbone diagram on the left. It illustrates logical relationships among frameworks for leadership, marketing management, and information systems, providing a detailed explanation.
Summary
Viscomi (2017) discusses the effectiveness of authoritative models, noting that executives are experts in their fields. However, Schnelle et al. (2021) suggest that authoritarian theory, which places communication under elite control, may not support this project. Glasius (2018) indicates that authoritarian practices shield power holders from accountability. Instead, the human relations theory would be more appropriate for addressing CapraTek’s business problems.
Summarizing three scholarly articles, the credibility, relevance, and applicability of authoritative models and theories for leadership, marketing, or information management concepts are assessed.
Appendix: Reflection on Feedback
Reflecting on feedback helped me identify my strengths and weaknesses. Initially, I was not open to feedback due to my previous academic achievements. However, embracing feedback allowed me to meet and exceed rubric guidelines. A crucial piece of feedback was to write the executive summary after completing the rest of the paper.
References
Anderson, C., Bieck, C., & Marshall, A. (2020). How business is adapting to COVID-19: Executive insights reveal post-pandemic opportunities. Strategy & Leadership, 49(1), 38–47. https://doi.org/10.1108/sl-11-2020-0140
Beer, M., Finnstrom, M., & Schrader, D. (2016, September 9). Why Leadership Training Fails—and What to Do About It. Harvard Business Review. https://hbr.org/2016/10/why-leadership-training-fails-and-what-to-do-about-it
Glasius, M. (2018). What authoritarianism is . . . and is not: a practice perspective. International Affairs, 94(3), 515–533. https://doi.org/10.1093/ia/iiy060
Goodhue, D. L., & Thompson, R. L. (1995). Task-Technology Fit and Individual Performance. MIS Quarterly, 19(2), 213. https://doi.org/10.2307/249689
Kokemuller, N. (2016, October 26). What Methods Can an Organization Utilize to Prevent Loss of Customers? Small Business – Chron.Com. https://smallbusiness.chron.com/methods-can-organization-utilize-prevent-loss-customers-80038.html
Kotler, K., Armstrong, G., Wang, V., & Saunders, J. (2022). Principles of Marketing (5th ed.). Pearson Education International.
Li, T. C., & Chan, Y. E. (2019). Dynamic information technology capability: Concept definition and framework development. The Journal of Strategic Information Systems, 28(4), 101575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsis.2019.101575
Morgan, B. (2021, December 10). Companies That Failed At Digital Transformation And What We Can Learn From Them. Forbes. https://www.forbes.com/sites/blakemorgan/2019/09/30/companies-that-failed-at-digital-transformation-and-what-we-can-learn-from-them/?sh=4d4bff8a603c
Rehman, N., Mahmood, A., Ibtasam, M., Murtaza, S. A., Iqbal, N., & Molnár, E. (2021). The Psychology of Resistance to Change: The Antidotal Effect of Organizational Justice, Support and Leader-Member Exchange. Frontiers in Psychology, 12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.678952
Ryba, K. (2021). How to Align Individual, Team, and Organizational Goals for Success. Quantum Workplace. https://www.quantumworkplace.com/future-of-work/how-to-align-organizational-goals
Schnelle, C., Baier, D., Hadjar, A., & Boehnke, K. (2021). Authoritarianism Beyond Disposition: A Literature Review of Research on Contextual Antecedents. Frontiers in Psychology, 12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.676093
Viki, T. (2018, September 26). The Three Human Barriers To Digital Transformation. Forbes. https://www.forbes.com/sites/tendayiviki/2018/09/23/the-three-human-barriers-to-digital-transformation/?sh=4565af45164b
Viscomi, C. (2020, August 30).7 New Types of Leadership Models for Innovative Thinkers. Aliste Marketing. https://alistemarketing.com/blog/types-of-leadership-models/
Wolf-Detwiler, M. (2021, August 27). Restaurant leaders share insight on top challenges, how to succeed. Fast Casual. https://www.fastcasual.com/articles/what-areas-do-restaurant-leadership-often-overlook/
Yukl, G. (2011). The SAGE Handbook of Leadership. Google Books. https://books.google.nl/books?hl=en&lr=&id=cvRg6tbxw9gC&oi=fnd&pg=PA286&dq=research+on+Contingency+theories&ots=QGCgZ6H5K6&sig=njTNcQihBqksNrbCXUyiwTIIn2A&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q=research%20on%20Contingency%20theories&f=false
Post Categories
Tags
- Annotated Bibliography (2)
- Bioinformatics (1)
- Budget Negotiations (1)
- Capital Budget (1)
- Capstone Video Reflection (1)
- Care Coordination (6)
- Community Health Care (1)
- Community Health Needs (1)
- Community Resources (2)
- Complaint Analysis (4)
- Concept Map (2)
- Curriculum Evaluation (1)
- Curriculum Overview (1)
- Dashboard Metrics Evaluation (1)
- Descriptive Statistics (1)
- Disaster Plan (1)
- Educational Technology (4)
- Enhancing Quality and Safety (1)
- Environmental Analysis (1)
- Evaluating Technology Usage (1)
- Evaluation Plan Design (1)
- Evidence and Resources (1)
- Evidence Based Approach (1)
- Evidence Based Care (1)
- Evidence-Based Change (1)
- Evidence-based Practice (1)
- Evidenced-Based Literature (2)
- Executive Summary (1)
- Exploration of Regulations (1)
- Final Project Submission (1)
- Global Issue (1)
- Health Care (3)
- Health Care Professional (1)
- Health Improvement Plan (1)
- Health Policy Proposal (1)
- Health Promotion Plan (3)
- Healthcare Improvement (2)
- Implementation Plan (2)
- Interdisciplinary Issue Identification (1)
- Interdisciplinary Plan Proposal (1)
- Intervention Strategy (1)
- Leadership and Group Collaboration (2)
- Leadership Reflection Video (1)
- Legal and Ethical Issues (1)
- Literature Review (1)
- Literature Search (1)
- Literature Synthesis (1)
- Managing the Toxic Leader (1)
- Manuscript for Publication (1)
- Media Submission (1)
- Meeting with Stakeholders (1)
- Mentor Interview (1)
- MSN Reflection (1)
- Near-Miss Analysis (1)
- Nurse Educator (1)
- Obesity (2)
- Ontological Humility (1)
- Organizational Change (1)
- Outcome Measures (1)
- Outcomes of the Intervention (1)
- Patient Care Plan (1)
- Patient Care Technology (1)
- Personal Leadership Portrait (2)
- PICOT (3)
- Policy Proposal (1)
- Political Landscape Analysis (1)
- Practicum and Social Justice (1)
- Professional Development (1)
- Professional Development Plan (1)
- Project Charter (4)
- Quality Improvement Proposal (4)
- Quality Performance Improvement (1)
- Research Skills (1)
- Risk Mitigation (1)
- Rubric Development (1)
- Safety Gap Analysis (1)
- Safety Improvement Plan (1)
- Scholarly Article (1)
- Scholarly Sources (2)
- Staff Training Session (1)
- Stakeholder Meeting (1)
- Stakeholder Presentation (1)
- Strategic Plan Appraisal (1)
- Strategic Plan Development (1)
- Strategic Planning (1)
- Technological Changes (1)
- Transitional Care Plan (1)
- Tripartite Model (1)

